
Top AI Metrics for Workflow Optimization
Healthcare Technology
Updated Jan 18, 2026
Key AI metrics: response time, resolution rate, appointment conversion, throughput and error rates to measure and optimize healthcare workflows and ROI.
AI in healthcare can transform workflows and improve efficiency - but only if you track the right metrics. Without measurement, AI systems risk becoming guesswork, leading to lost revenue and poor patient experiences. Here’s what you need to know:
Response Time: Faster responses reduce patient frustration and abandonment rates. Aim for under 1 second to improve engagement.
Resolution Rate: High task completion without human help saves time and money.
Appointment Conversion: Tracks how many inquiries turn into bookings, directly impacting revenue.
Patient Throughput Rate: Measures how many patients your practice can handle daily, highlighting bottlenecks.
Error Analysis: False Positives and False Negatives can skew results. Use precision and recall metrics to fine-tune AI accuracy.
Efficiency Metrics: Monitor time savings, cost per interaction, and staff workload reductions to gauge AI’s impact.
Tracking these metrics ensures your AI systems deliver measurable results, from reduced call abandonment to better patient access. Without proper monitoring, you risk inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
How to Assess Machine Learning Models: AUC, F1 and more (clearly explained) // #6 of ML for Health
Core AI Metrics for Workflow Optimization
Tracking the right metrics can turn AI from a costly experiment into a game-changing asset. Below, we dive into four key performance metrics that can optimize AI's role in healthcare.
Response Time
Response Time measures how quickly an AI system responds after a patient reaches out - whether through a call, chat, or text. This metric is crucial for distinguishing quick, effective assistance from frustrating delays that lead to patient abandonment. Ideally, AI systems should respond within 0.1 to 1.0 seconds[1]. Delays beyond this range can harm patient engagement and increase call abandonment rates.
The financial impact of slow response times is no small matter. For instance, a healthcare practice managing 2,000 calls a day with a 7% abandonment rate could lose around $45,000 in daily revenue[4]. Compare this to traditional call centers, where hold times average 4 minutes and 24 seconds - far longer than the Healthcare Financial Management Association's recommended 50-second standard[4].
"For decades, patients have been largely passive partners in their own healthcare. Those days are over. Patients empowered by technology and a new sense of autonomy are shopping for providers the way they do for other services and demanding that clinicians accommodate their expectations for scheduling, service and technology." - Gary Hamilton, CEO, Intelichart[4]
To improve Response Time, consider strategies like monitoring peak usage periods, caching frequently asked questions, and streamlining backend processes. While industry benchmarks suggest an Average Speed of Answer around 28 seconds[6], AI systems should aim to eliminate wait times altogether.
Resolution Rate
Resolution Rate measures how many tasks the AI completes without needing human intervention. These tasks can include appointment scheduling, lead capture, or insurance verification. A high Resolution Rate reduces the burden of repetitive administrative work, freeing up staff for more critical clinical responsibilities[7][8].
The financial benefits are clear: AI-powered scheduling tools can save hospitals between $100,000 and $140,000 annually by cutting labor costs[9]. In surgical settings, AI has achieved 95% accuracy in identifying procedural milestones, reclaiming 15–30 minutes of idle time per operating room each day[9]. On the flip side, a contact center abandonment rate above 10% signals inefficiencies that need urgent attention[10].
Beyond completing tasks, converting inquiries into appointments is another vital aspect of this metric.
Appointment Conversion
Appointment Conversion tracks how many patient inquiries result in scheduled appointments through the AI system. This metric ties AI performance directly to revenue, as every converted inquiry represents income that might otherwise slip away.
Low conversion rates often point to issues like long hold times, overly complicated scheduling processes, or limited after-hours availability. AI systems that operate 24/7/365 can address these challenges by removing capacity constraints and capturing opportunities that might be missed during traditional office hours.
AI-based recommendations can increase conversion rates by 20% to 30%[1], and top-performing organizations have reported a 13% ROI on AI investments, compared to an enterprise average of 5.9%[1]. To maximize this metric, integrate AI with your EHR system to provide real-time scheduling, use sentiment analysis to prioritize high-intent patients, and enable direct calendar booking during the first interaction[4][11].
Tracking where inquiries originate and tailoring the AI's approach for each channel can further enhance conversion rates.
Patient Throughput Rate
Patient Throughput Rate measures how many patients your practice can handle daily or per session. By streamlining scheduling, triage, and administrative workflows, AI can boost this number without requiring additional staff or physical space.
Higher throughput means more revenue and better patient access. When AI automates tasks like intake forms, insurance verification, and appointment confirmations, your team can focus on providing care instead of managing paperwork.
Tracking Patient Throughput alongside Response Time and Resolution Rate can help identify bottlenecks. For example, if the AI delivers quick responses and resolves tasks effectively but throughput remains flat, the issue might lie in downstream processes - like exam room availability, provider schedules, or post-visit workflows. This data can also support decisions about capacity investments and provide clear ROI evidence for stakeholders.
Understanding False Positives and False Negatives
Relying on accuracy alone can give practice managers a false sense of security. Accuracy treats all errors as if they’re the same, which doesn’t capture the complexity of healthcare operations. Imagine an AI model boasting 99% accuracy - it sounds impressive, right? But if the model is screening for a rare condition that occurs in just 1% of cases, it could hit that score by simply predicting "negative" for every patient. In this scenario, the AI completely misses its purpose [12][13].
To truly evaluate performance, you need to understand the different types of errors. Specifically, False Positives (flagging non-urgent cases as urgent, like routing a routine appointment to an emergency triage team) and False Negatives (missing urgent cases, such as failing to escalate a patient reporting chest pain) [12][13].
"Accuracy can be a misleading metric for imbalanced datasets: in a dataset with only 1% positive cases, a model that always predicts negatives would have 99% accuracy." – John H Cabot, MD, Stanford University School of Medicine [13]
A Confusion Matrix offers a better way to track and visualize these errors. It categorizes predictions into True Positives, True Negatives, False Positives, and False Negatives. This breakdown allows you to calculate more insightful metrics like Precision (how often "urgent" predictions were correct) and Recall (how many urgent cases were successfully identified). For more detailed calculations and templates, check out this Confusion Matrix guide. Understanding these metrics is key to improving operational efficiency.
Why False Positives Matter
False Positives may seem harmless at first glance, but they can create significant operational headaches. When your AI mistakenly escalates non-urgent cases, it sets off unnecessary actions: specialists waste time reviewing routine issues, and administrative staff spend hours on follow-ups that lead nowhere.
The financial toll can be substantial. Each false alarm diverts valuable staff time that could be focused on urgent cases or revenue-generating tasks. In healthcare customer service, even a modest 5% improvement in model accuracy can reduce repeat inquiries and improve patient satisfaction [1]. But the costs don’t stop there. False Positives can also lead to unnecessary tests and procedures. As Dr. John H Cabot from Stanford University School of Medicine explains, "A highly-sensitive cancer diagnostic tool could facilitate early detection of cancers, but false positives could lead to more unnecessary biopsies, anxiety, and healthcare costs" [13].
The Impact of False Negatives
False Negatives, on the other hand, can have far more serious consequences. Missing urgent cases not only risks patient harm but also leads to lost revenue. For example, if your AI fails to recognize a high-priority appointment inquiry or a critical health issue, those cases may slip through the cracks without proper escalation or follow-up [12][13].
The ripple effects of False Negatives extend beyond individual cases. While industries like retail resolve 74% of customer inquiries on the first call, healthcare lags far behind, resolving only 20% on the first attempt due to the complexity of cases and limited tools [5]. False Negatives exacerbate this problem, forcing patients to repeatedly contact your practice, raising abandonment rates, and potentially damaging your reputation.
When fine-tuning your AI system, you’ll often face a balancing act. Lowering the threshold to catch more urgent cases (reducing False Negatives) usually increases False Positives. Conversely, raising the threshold to avoid false alarms may let more urgent cases go unnoticed [12]. This trade-off underscores the importance of carefully monitoring and adjusting your AI's performance metrics.
Operational Efficiency Metrics
Once you've refined accuracy through error rate analysis, it's time to evaluate AI's measurable impact on cost and time savings. These efficiency metrics, alongside core performance indicators, highlight how AI simplifies healthcare operations. They bridge the gap between AI capabilities and tangible improvements in day-to-day workflows.
Processing Time Reduction
Average Handle Time (AHT) measures the total time spent on a task, including talk time, hold time, and post-call work. In healthcare, the baseline is striking: the average hold time for human-only call centers is 4 minutes and 24 seconds - five times longer than the 50-second benchmark recommended by the Healthcare Financial Management Association [4].
AI steps in to automate tasks like insurance verification and appointment confirmations, slashing interaction times by as much as 50% [14]. For instance, if confirming an appointment manually takes 3 minutes but drops to 90 seconds with AI, that's a 50% time reduction.
However, speed alone isn't enough. Monitor AHT alongside First Call Resolution (FCR) and satisfaction scores to ensure faster processing doesn't come at the expense of quality. While retail call centers achieve an FCR of 78% and general call centers average 71%, healthcare struggles with only 20% of medical calls resolved on the first attempt [5].
Staff Time Savings
After Call Work (ACW) refers to the administrative tasks that follow patient interactions, such as updating electronic health records (EHRs), documenting notes, and handling paperwork. This is where AI delivers substantial relief. For example, in 2023, Singing River Health System adopted Dragon Medical One and PowerMic Mobile to improve clinical documentation workflows. Under the leadership of Dr. Clinton Hull, the system saw an 88% adoption rate across the organization [15].
"One of the things that's helped providers, including myself, become more efficient and save even more time with Dragon Medical One are the shortcuts that do repetitive actions a lot faster than finding and clicking on things or typing in long paragraphs of text." – Clinton Hull, MD, Medical Director of Clinical Informatics, Singing River Health System [15]
AI's ability to reduce ACW through high containment rates (80–90% of cases resolved by AI) allows staff to focus on higher-value clinical tasks [1][2]. This is especially critical given the staffing shortages in healthcare. At peak levels, call centers typically meet only 60% of the required staffing coverage, leaving a gap that AI can help bridge [4].
Cost Savings
The financial benefits of AI become evident when you calculate the Cost per Resolved Interaction. Compare AI's operational costs (infrastructure, API usage, data storage) with the human labor formula: (AHT × Staff Cost per Minute) + Rework Costs [2]. AI can reduce service costs by 20–30% and cut the cost per conversation in half [1]. Once scaled, organizations often aim for a 20–40% reduction in unit costs, depending on task complexity [2].
AI also protects revenue. For healthcare practices handling 2,000 calls daily, a 7% call abandonment rate can lead to significant losses. With 60% of patients hanging up after waiting more than one minute, this translates to an estimated $45,000 in lost daily revenue [4]. By answering 100% of calls instantly, AI eliminates this revenue leakage. To track ROI, measure both the direct cost savings and the revenue preserved through improved patient access.
Comparing AI Performance with Baseline Metrics
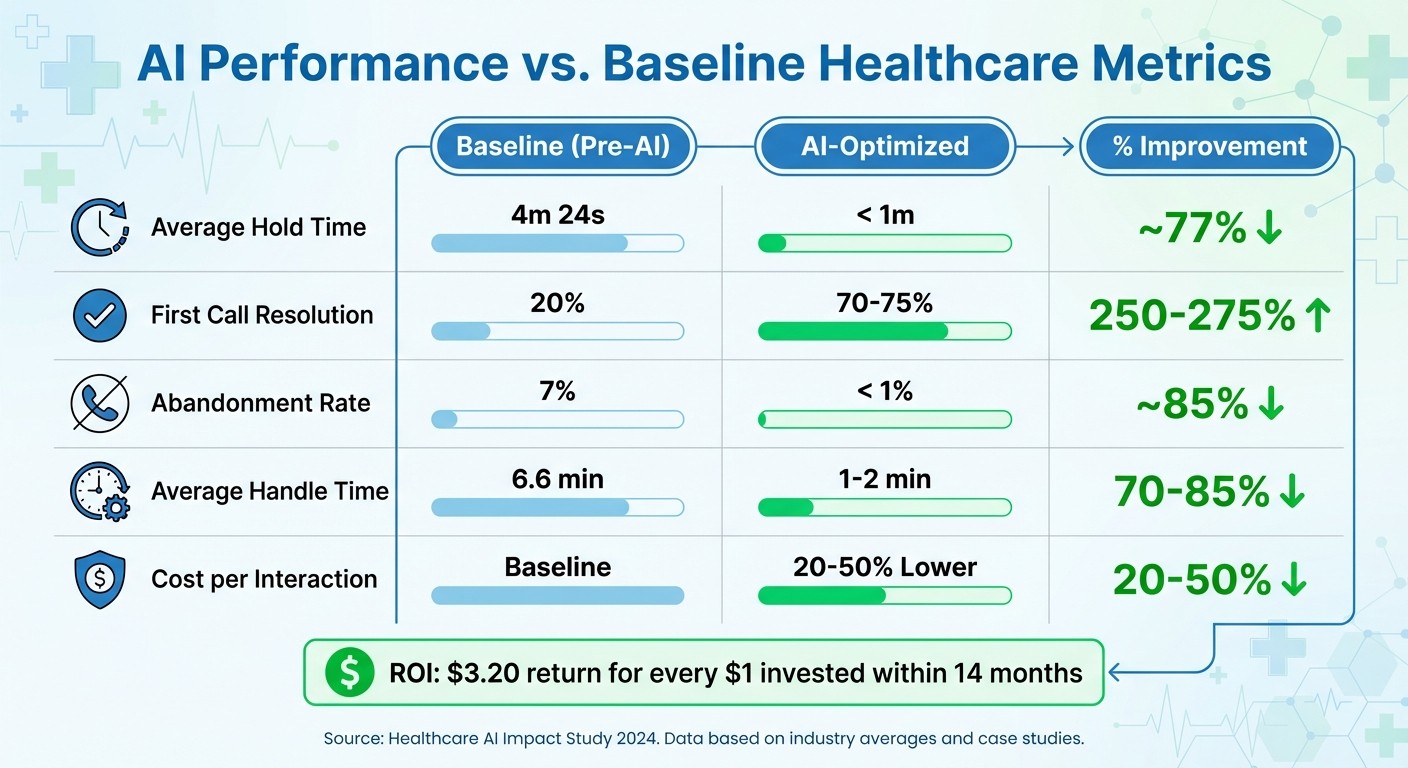
AI vs Traditional Healthcare Metrics: Performance Comparison
To truly understand the value of your AI investment, comparing its performance against baseline metrics is essential. This kind of analysis helps demonstrate the impact of AI to stakeholders in a clear, data-driven way. A straightforward method is to use a four-column comparison table: Metric, Baseline (Pre-AI), AI-Optimized, and % Improvement.
The formula for calculating improvement varies depending on the metric type:
For metrics where lower numbers are better:
((Baseline – AI Value) / Baseline) × 100For metrics where higher numbers are better:
((AI Value – Baseline) / Baseline) × 100[18].
This percentage change can make a strong case for AI adoption, especially for practice managers and CFOs. Below is an example of how AI can improve key operational metrics:
Metric | Baseline (Pre-AI) | AI-Optimized | % Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
Average Hold Time | 4m 24s | < 1m | ~77% |
First Call Resolution | 20% | 70–75% | 250–275% |
Abandonment Rate | 7% | < 1% | ~85% |
Average Handle Time | 6.6 min | 1–2 min | 70–85% |
Cost per Interaction | Varies | 20–50% Lower | 20–50% |
When implemented effectively, organizations report a $3.20 return for every $1 invested in AI within just 14 months [19]. However, achieving these results requires consistent monitoring and adjustment.
Tracking and Visualizing Improvements
To fully validate AI performance, real-time tracking is key. Start by establishing a solid measurement framework before deploying AI. This means gathering at least 30–90 days of historical data from sources like EHR audit logs, phone system reports, and scheduling software [3][4]. Without these baselines, accurate performance comparisons are impossible.
Real-time dashboards are much more effective than quarterly reports. Use tools like Service Level Objectives (SLOs) to set alerts for performance deviations. For example, you might track if the AI-to-human handoff rate exceeds 20% or if response latency increases over three consecutive weeks [2]. Despite 80% of enterprises listing reliability as a top concern, only 35% actively monitor AI performance metrics [1]. Don’t fall into that gap.
To turn raw metrics into meaningful insights, segment your data by factors like input type, time of day, and patient demographics [3]. For instance, a 90% containment rate might sound impressive, but it’s less so if patients are repeatedly calling back the next day due to unresolved issues. Pair technical metrics with Patient Satisfaction (PSAT) scores and First Call Resolution (FCR) rates to ensure the AI is truly solving problems, not just deflecting them [16].
"Patient access isn't a feature anymore. It is fundamental to how providers operate, run their business, and support their community." – Jeff Gartland, CEO, Relatient [20]
Conclusion
Tracking AI performance is more than just a good practice - it's the backbone of effective workflow optimization. Ian Heinig, Agentic AI Marketer at Sendbird, sums it up perfectly: "AI metrics are where the guesswork of AI strategy meets scientific and operational rigor" [1]. Without proper measurement, you’re essentially flying blind, unable to demonstrate ROI or pinpoint where AI is helping versus hindering.
The numbers speak for themselves. Healthcare practices using AI report saving 10–14 staff hours daily and reducing service costs by 20–30% [1][17]. Even a small improvement, like a 1% drop in call abandonment rates, can result in four extra patients each week [5]. These results highlight how tracking the right metrics can directly impact your bottom line.
But the focus needs to go deeper than surface-level metrics. For instance, response time only holds value when paired with First Contact Resolution, and accuracy must factor in both false positives and negatives. These nuanced insights reflect the balance between speed, resolution, and error accuracy discussed earlier.
Tools like Lead Receipt can help automate tasks such as call handling, scheduling, and lead management, turning AI into a strategic asset rather than just another expense.
The real question isn’t whether you should track AI metrics - it’s whether you can afford not to. With 80% of enterprises prioritizing AI reliability but only 35% actively monitoring performance [1], the gap presents a major opportunity. By establishing clear baselines, monitoring regularly, and letting data guide your decisions, you can transform AI into a game-changer for your practice.
FAQs
How does AI help healthcare practices improve appointment bookings?
AI-driven systems streamline appointment booking by managing patient inquiries instantly, verifying details like insurance or referrals, and scheduling appointments in real time. Unlike human staff, these systems operate 24/7, making it possible for patients to book appointments even after regular office hours. This around-the-clock availability can result in a 10–15% increase in booking rates. Additionally, AI tools send tailored reminders before appointments, which helps cut down on no-shows and ensures schedules stay on track.
One standout feature is the ability to differentiate between urgent and non-urgent requests. This ensures that patients with critical needs are prioritized, while routine inquiries are handled promptly and efficiently. The result? A smoother patient experience and a higher likelihood of successful bookings.
Key Metrics to Monitor
Response Time: AI should respond to patient inquiries in under 30 seconds.
Booking Rate: Track how many inquiries are successfully converted into appointments.
Reminder Impact: Measure the drop in no-show rates after sending AI-generated reminders.
Integrating tools like Lead Receipt can simplify these processes further. These solutions work seamlessly with your current systems and provide actionable insights to fine-tune performance.
Why is it important to track AI metrics in healthcare workflows?
Not keeping tabs on AI metrics in healthcare workflows can lead to a host of problems - inefficiencies, mistakes, and even financial setbacks. Metrics like response time, resolution rate, and appointment conversion provide crucial insights. Without them, it’s hard to pinpoint workflow bottlenecks or evaluate how well AI tools are working. The result? Longer patient wait times, more no-shows, and a noticeable hit to revenue.
Focusing only on overall accuracy can also be misleading. Take false positives, for example - they might flag non-urgent calls as urgent, wasting valuable staff time. On the flip side, false negatives could miss real emergencies, putting patient safety at risk. Regularly reviewing performance data helps catch these issues early and ensures AI systems stay dependable. It also prevents problems like model drift, where performance gradually declines over time.
Bottom line: tracking the right metrics isn’t just about fine-tuning workflows - it’s about enhancing patient experiences, boosting satisfaction, and proving ROI to stakeholders. It’s a must for keeping operations running smoothly.
What are False Positives and False Negatives, and how do they affect AI performance in healthcare?
False Positives (FP) and False Negatives (FN) are two types of errors that can significantly affect how well AI systems perform in healthcare. A False Positive happens when the AI mistakenly flags something as urgent when it’s not - like treating a routine patient inquiry as an emergency. This can lead to unnecessary use of resources, longer wait times, and increased costs. On the flip side, a False Negative occurs when the AI misses a real issue, such as failing to detect an actual emergency. This kind of error can delay critical care, jeopardize patient safety, and even open up liability risks.
These errors also distort key workflow metrics like response time, resolution rate, and appointment conversion rates, making it harder to streamline operations. By carefully analyzing FPs and FNs, healthcare managers can find the right balance: prioritizing the reduction of FNs to safeguard patient well-being while also working to lower FPs to enhance efficiency. Tools like confusion matrices are invaluable for visualizing these errors and refining AI systems for improved outcomes.
